Planning and prioritization are one of the most important tasks of a Technical Product Manager. In this way, it is ensured that the final product remains within the framework of the drawn vision and scope, and the plans are followed. By defining and prioritizing the work to be done in each step, it is ensured that the value of the product is maximized during the process, from the starting point to the target. The steps that a Technical Product Manager should follow in the planning and prioritization process are:
Gathering necessary information from stakeholders. After the vision and strategy of our project has been determined, the requirements, which are the first step towards the realization of the project, should be collected within this scope. All stakeholders should be involved in gathering requirements. Here, the stakeholder does not mean only customers, but also the technical team, sales and marketing teams and other existing teams should be evaluated among the stakeholders for which information will be collected. The reason for including different stakeholders in the process is to evaluate both the problem and the solution to this problem with data obtained from different sources, and to determine the focus of the product and to make sure that it does not deviate from the target.
In a presentation1 made by Elizabeth LARSON in 2014, it was stated that 47% of projects whose requirements were not well defined could not reach their targets. In projects where the requirements are not gathered correctly and well expressed, there is always the risk of an uncontrolled growth of the scope in the advancing processes. In addition, in a project that does not progress correctly, the work that has been done before will need to be redone or corrected. In addition, teams working in an unclear context will often experience confusion, restlessness, and loss of motivation.
The requirements to be collected can be divided into business and technical requirements. While the business requirements focus on the solution that the project will bring to the problem, the technical requirements focus on the performance, reliability and usability of the identified business requirements. Details such as platform(s), software language, database and architecture to be developed within the framework of technical requirements are determined.
Identifying and prioritizing product features. It is perhaps the most important task of the Technical Product Manager in maximizing product value. The issues determined in the vision and planning are clarified in more detail and correctly prioritized in order to maximize the value to be added during the development phases of the product.
The biggest assistants of a Technical Product Manager in the identification and prioritization processes can be listed as Story Mapping, Impact Mapping and Story Prioritization. To briefly mention these;
Story Mapping: It is based on separating the features of the product into more manageable user stories and visualizing the roadmap to make it more understandable for the team. It provides a holistic view of the product at a glance and helps the team understand and develop a parallel understanding of user needs and priorities.
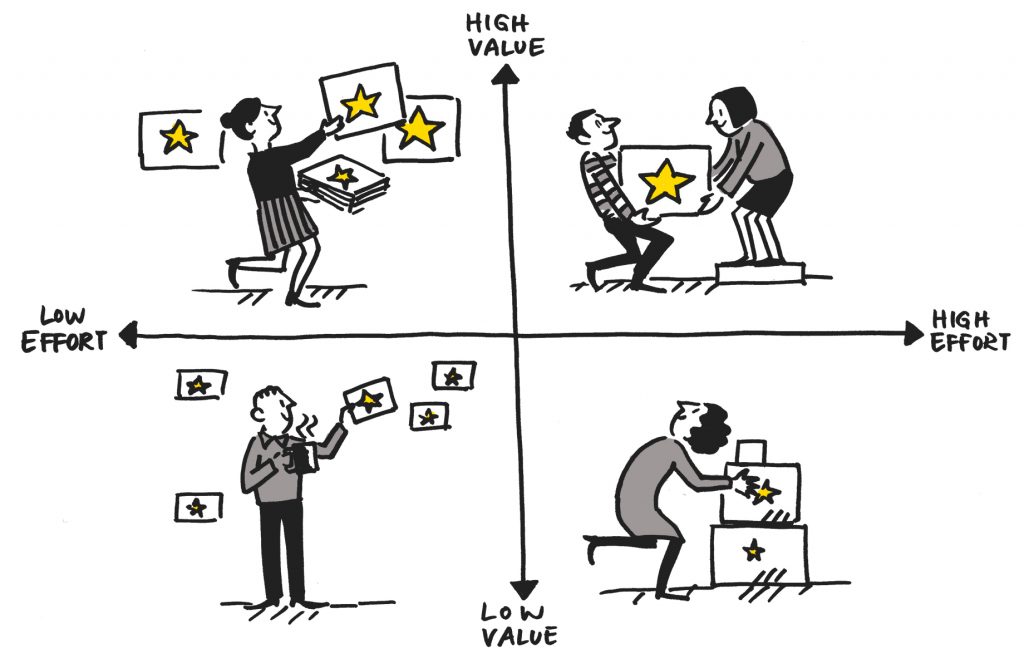
The story map is drawn in two independent dimensions, vertical and horizontal. The vertical axis ranks the stories in order of priority and importance, while the horizontal axis places the stories in order of development. This chart, which will be updated within the framework of changing and developing needs, offers an interface that is easier to read and understand than the more static requirement list.
The following steps are followed for story mapping:
- The main target or final result about the product is determined.
- Key processes and tasks used by the end user to achieve the goal are defined.
- User stories are placed horizontally on the timeline based on their activity. Each user story is divided into smaller and more detailed sub-breakdowns or sub-stories and placed below the user stories to which they belong, on the vertical axis.
- User stories are prioritized according to their importance and updated with feedback and new information throughout the project.
Impact mapping: Impact mapping is the act of identifying the desired outcomes and matching them with features or actions to achieve these outcomes with the aim of maximizing the product possible. In this way, it is presented visually which actions to reach the goal will be prioritized and how.
The following steps are followed for impact mapping:
- The final result and benefit targeted by the product are clearly defined.
- Stakeholders and participants who contribute or have an impact on the goal are determined.
- The effects and changes necessary for each participant to reach the goal are determined.
- The characteristics and processes that will create the determined effects are set.
- The outputs to be presented are prioritized according to feasibility and importance.
Story prioritization: The process of prioritizing and ordering user stories and features to be presented. During this ranking, the value it will add to the user, business value, effort, dependency and constraints are taken into consideration.
The following methods can be used for story prioritization:
- Using the MoSCoW methodology (Must-have, Could-have, Won’t have) high priority and MVP (Most Viable Product) features are determined.
- The value added to the user is scored by weighting the business value, effort and risks. Prioritization is made according to the results.
- Using the Kano model, features are divided into three categories (Must-be, One-dimensional, Attractive) and prioritized according to the impact they have on the customer in terms of meeting the needs and level of satisfaction.
Shaping decisions with data: Data should always be the most powerful tool at a Technical Product Manager’s disposal when making product decisions. These data are data such as customer feedback, market research, usage statistics and customer loyalty. In this way, correct contributions can be made to the product development process and vision through objective data. It is one of the healthiest methods in determining the strengths and weaknesses of the product, the points that can be improved and the features to be added/removed.
How is data collected?
- By measuring usage statistics, user habits and other values with software such as Google Analytics, Mixpanel.
- Interviews with the end user, surveys, usability tests, and identification of user needs and problems.
- By receiving feedback and determining user preferences through support systems, feedback applications and social media monitoring.
- Through industry trends, competitors, market demand analysis and industry publications.
How is data interpreted?
- By resorting to quantitative analysis methods to analyze patterns, trends, and relationships. (Cohort analysis, Funnel analysis, User segmentation, Conversion rate analysis)
- With one-on-one interviews, feedback and support tickets, qualitative analysis methods will be used to determine the problems, preferences and motives of the user.
- With data visualization methods that will make the data at hand more understandable with tables and graphs.
Creating a roadmap: Once features have been identified and prioritized, the Technical Product Manager’s next step is to define a roadmap that outlines the steps leading up to product delivery. The roadmap should show key points on a timeline, and the estimated resource needs that will be required for each delivery. The roadmap shows the product vision in general and the goals for each stage in detail. The product map also represents an agreement within the framework of cooperation between the development teams and the Product management team.
The roadmap for a product may not be unique. Separate roadmaps can be developed according to the different needs of different stakeholders. The different types of roadmaps that can be considered within the framework of stakeholders can be listed as “Internal roadmap for development teams“, “Internal roadmap for senior management“, “Internal roadmap for sales team“, “External (for Customers) roadmap“.
Communicating with Stakeholders: Ensuring that the determined plan is clearly shared and understood with internal stakeholders helps to prevent possible work accidents in the future. The priorities and the contribution and impact of the work to be done on the whole product should be clearly understood by the team. Internal teams should not be understood only as the development team. Management along with the Marketing and Sales teams must follow the same path for the product to be successful. In this context, it is of great importance to keep vertical and horizontal communication channels active and alive both in general and within each team.